
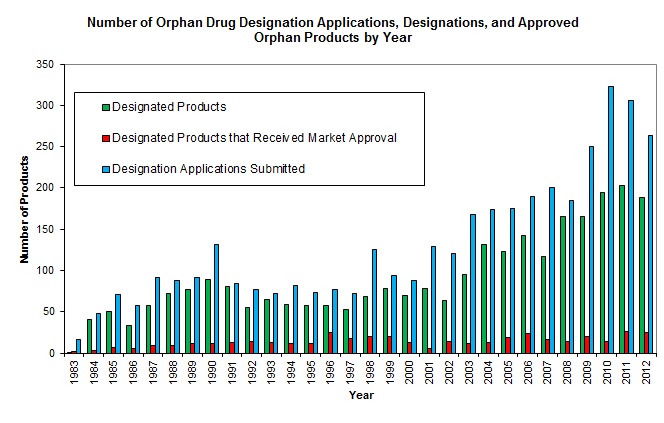
At that time, drug therapies for such diseases were rarely developed. The Orphan Drug Act (ODA), first enacted in the United States in 1983, was set up to encourage the development of drugs for rare diseases. Provenance: Commissioned not externally-peer reviewed


This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.įunding: MH is currently the Principal Investigator of Grant #EOG 123678 funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research entitled “Emerging Health Researchers and the Commercialization of Academic Science.” The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.Ĭompeting interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist. Citation: Herder M (2017) What Is the Purpose of the Orphan Drug Act? PLoS Med 14(1):Ĭopyright: © 2017 Matthew Herder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
